import matplotlib.pyplot as pl
import numpy as np☑ Plotting
1 Matplotlib
We will be covering key plotting APIs that will be very useful for visualization of machine learning data.
https://medium.com/mlpoint/matplotlib-for-machine-learning-6b5fcd4fbbc7
#
# an empty figure
#
fig = pl.figure(figsize=(3, 3))
pl.xlabel('X labels go here')
pl.ylabel('Y labels go here')
pl.xticks([0,1,2,3,4,5])
#
# get the axis object to set the tick labels
#
ax = pl.gca()
ax.set_xticklabels(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']);
pl.figure(figsize=(6,6))
x = np.linspace(-2*np.pi, 2*np.pi, 1000)
y1 = np.sin(x)
y2 = np.cos(x)
pl.plot(x, y1, color='red', linestyle='-')
pl.plot(x, y2, color='blue', linestyle='--')
pl.legend(['y1=sin(x)', 'y2=cos(x)'], loc='upper right');
2 Line plots
#
# Plotting line with annotation
#
x = np.linspace(-1, 1, 20)
y1 = np.abs(np.random.randn(20))
pl.plot(x, y1, '-o')
pl.text(x[10], y1[10], 'midpoint', fontsize=12);
#
# Area plot
#
pl.fill_between(x, y1, color='blue', alpha=0.1)
pl.plot(x, y1, linewidth=2, color='blue');
y2 = - y1 / 2
pl.fill_between(x, y1, y2, color='gray', alpha=0.5);
pl.plot(x, y1, x, y2, color='black', linewidth=2);
3 Bar Plots
names = ['Jack', 'Jill', 'Joe']
x = np.array([0, 1, 2])
grades = [70, 75, 80]
pl.bar(x, grades)
pl.xticks(x, names);
grades_winter = [95, 95, 90]
pl.bar(x+0.00, grades, width=0.25, label='Fall')
pl.bar(x+0.25, grades_winter, width=0.25, label='Winter')
pl.ylim(None, 120)
pl.legend(loc='upper left');
#
# final, midterm, quiz
#
grades = np.array([
[30, 30, 10],
[50, 30, 15],
[45, 23, 5],
])
pl.bar(x, grades[:, 0], label='final')
pl.bar(x, grades[:, 1], bottom=grades[:, 0], label='midterm', )
pl.bar(x, grades[:, 2], bottom=grades[:, :2].sum(axis=1), label='quiz')
pl.legend()
pl.xticks(x, names);
4 Scatter Plots
n = 500
x = np.random.randn(n)
y = np.random.randn(n)
pl.scatter(x, y, s=10);
#
# with size variation
#
size = np.abs(np.random.randn(n)) * 30
pl.scatter(x, y, s=size, alpha=0.4, linewidth=0);
#
# with color variation
#
colors = np.full((n,), '#f00')
colors[x <= y] = '#0f0'
pl.scatter(x, y, s=size, c=colors, alpha=0.4, edgecolors='none');
5 More to come
As we proceed further with the topics of machine learning, we will encounter more mathematical objects and ways to show them graphically.
We will look at:
- generate meshgrids
- contour plots of potential functions
- quiver plots for field functions
- 3D plots for higher dimensional datasets
6 Contours
Suppose we have the following potential function over the 2D space.
\[ z = \sin(\sqrt{x^2 + y^2}) \]
We want to compute the potential function in the region of \([-10, 10]\) by \([-10, 10]\).
xs = np.linspace(-10, 10, 100)
ys = np.linspace(-10, 10, 100)
zs = np.zeros((100, 100))
Warning
Do not use loop.
#
# You should not be doing this.
#
for i in range(xs.size):
for j in range(ys.size):
zs[i,j] = np.sin(np.sqrt(xs[i]**2 + ys[j]**2))
zs.shape(100, 100)
Note
The proper way is to use meshgrid.
X, Y = np.meshgrid(xs, ys)
X.shape, Y.shape((100, 100), (100, 100))Z = np.sin(np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2))
Z.shape(100, 100)pl.contour(X, Y, Z, levels=15, cmap='gray')<matplotlib.contour.QuadContourSet at 0x7ff4e1f9b820>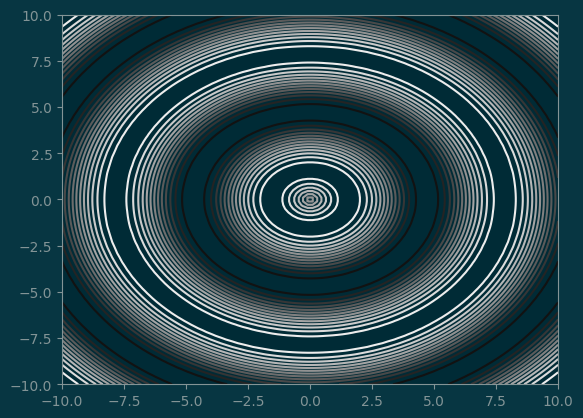
pl.contourf(X, Y, Z, levels=15, cmap='jet');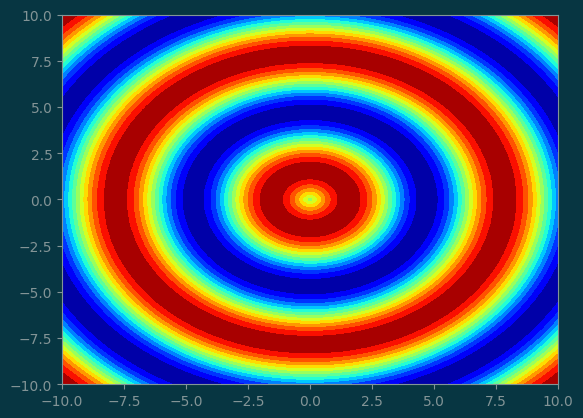
pl.contourf(X, Y, Z, levels=[np.min(Z), np.mean(Z), np.max(Z)], cmap='jet');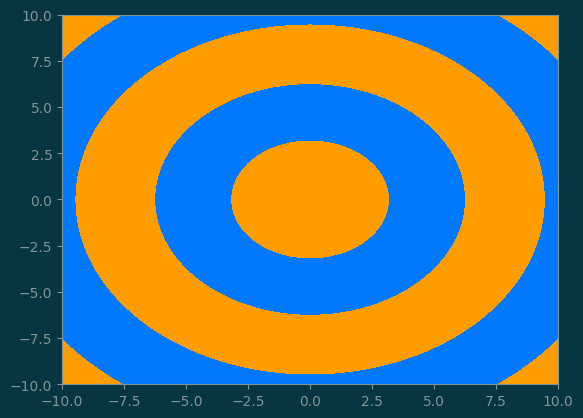
7 Vector fields
X, Y = np.meshgrid(
np.linspace(-5, 5, 10),
np.linspace(-5, 5, 10)
)
u = 1
v = -1
pl.quiver(X, Y, u, v, color='white');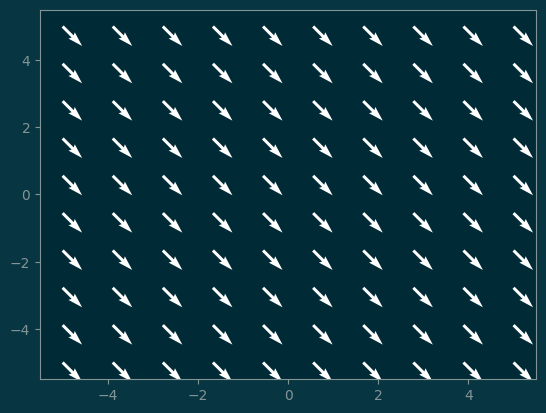
u = X
v = Y
pl.quiver(X, Y, u, v, color='white');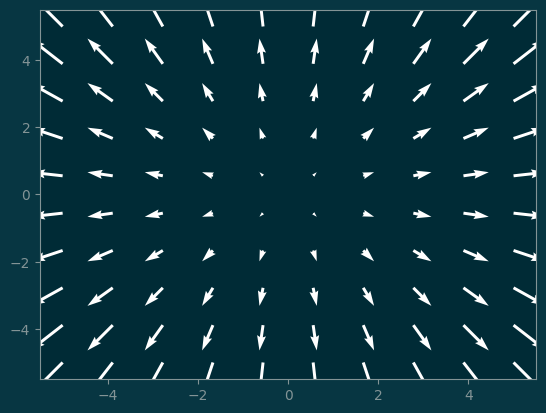
Here is a call vector field:
\[ \vec F(x, y) = -\frac{y}{\sqrt{x^2+y^2}}\mathbf{i} + \frac{x}{\sqrt{x^2+y^2}}\mathbf{j} \]
u = -Y / np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2)
v = X / np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2)
pl.quiver(X, Y, u, v, color='white');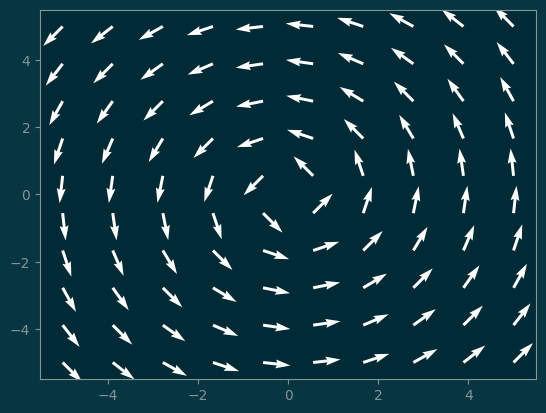
8 3D plot points and lines
from mpl_toolkits import mplot3dfig = pl.figure()
ax = pl.axes(projection='3d')
ax = pl.axes(projection='3d')
zs = np.linspace(0, 15, 1000)
xs = np.sin(zs)
ys = np.cos(zs)
ax.plot3D(xs, ys, zs, linewidth=2, color='red');
z2 = np.random.random(100) * 15
x2 = np.sin(z2) + 0.1 * np.random.random(100)
y2 = np.cos(z2) + 0.1 * np.random.random(100)
ax.scatter(x2, y2, z2, c=z2, cmap='jet');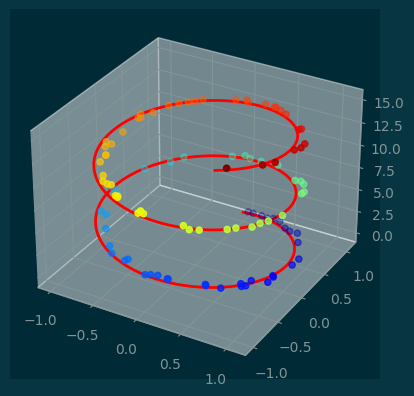
9 3D Contours
xs = np.linspace(-6, 6, 30)
ys = np.linspace(-6, 6, 30)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(xs, ys)
Z = np.sin(np.sqrt(X ** 2 + Y ** 2))X.shape, Y.shape, Z.shape((30, 30), (30, 30), (30, 30))ax = pl.axes(projection='3d')
ax.contour3D(X, Y, Z, levels=100, cmap='jet')
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y')
ax.set_zlabel('z');
## ax.view_init(60, 35);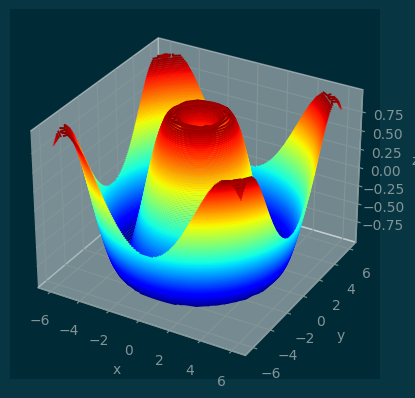
#
#
#